Introduction
A suitable pH environment is critical for bacterial survival; while determining optimal pH aids culture media preparation, traditional experimental methods are labor-intensive, material-wasting and time-consuming, and most bacteria remain unculturable due to unknown media, necessitating a new approach. Machine learning, as a preferred alternative in recent years, builds prediction models based on expanding high-throughput sequencing data and existing experimental pH data to supplement optimal pH determination—resolving experimental limitations, promoting massive data utilization, and offering references for alleviating the imbalance between sequencing and experimental measurement rates in other bacterial environmental preference studies.
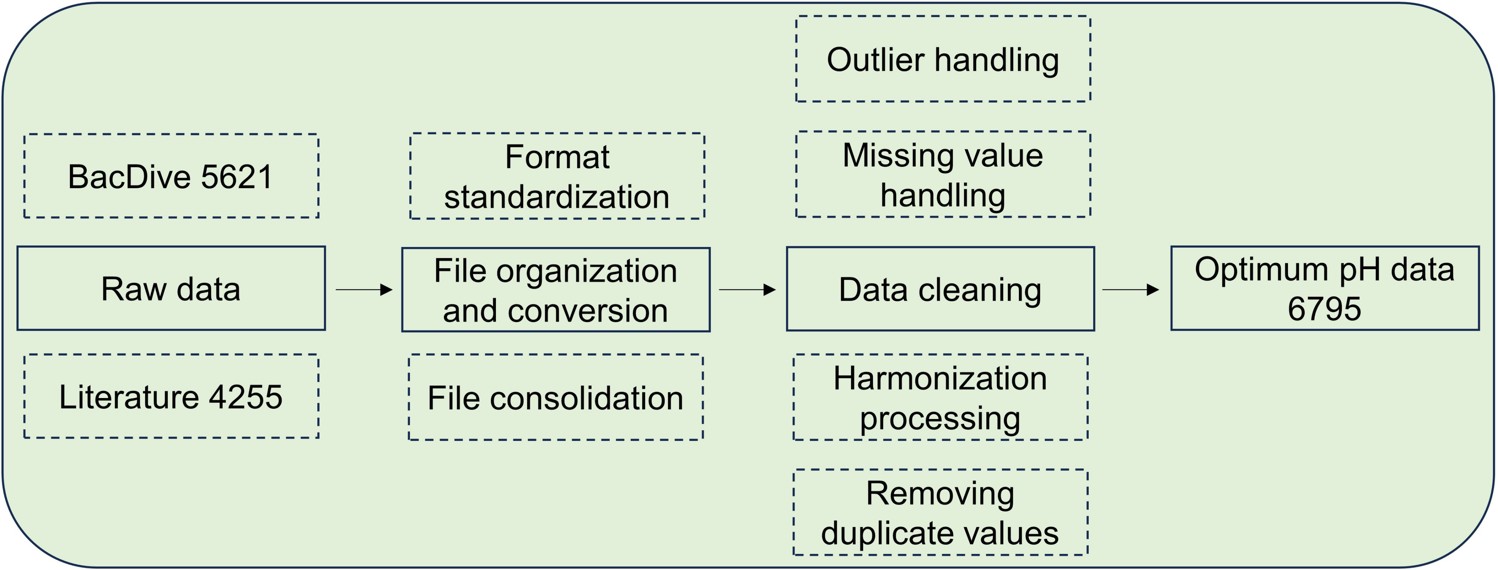
Flowchart for the collection and pre-processing of public microorganisms' optimal growth pH big data
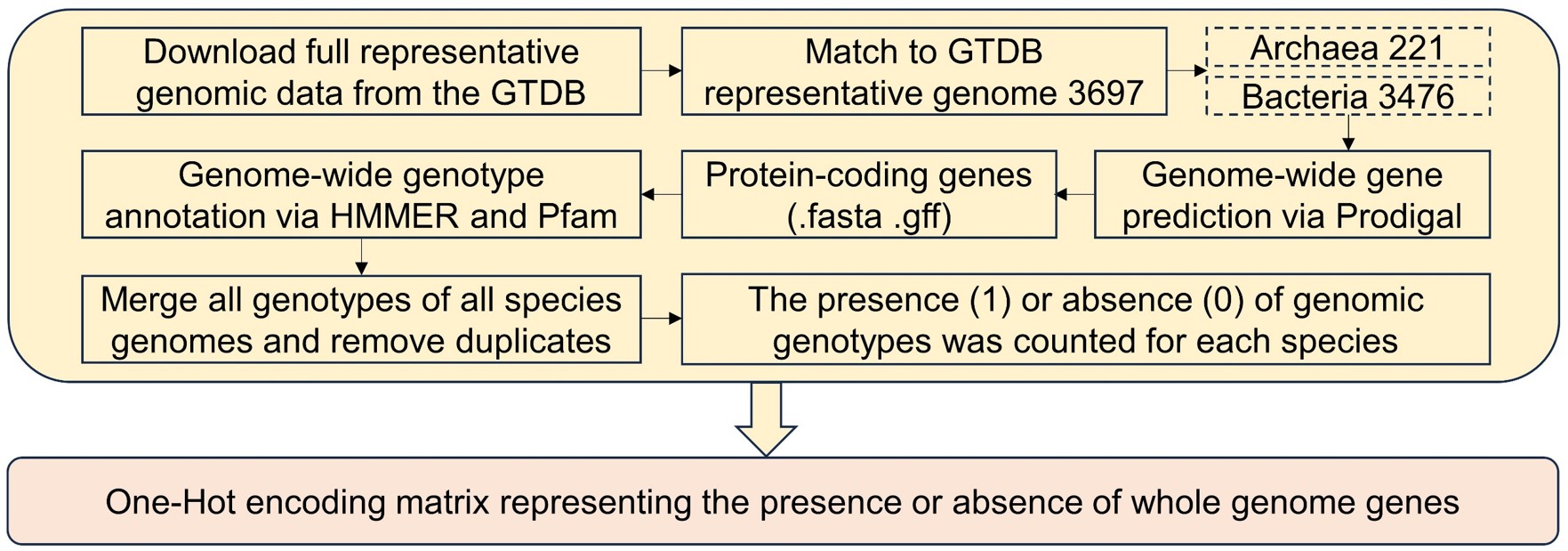
Acquisition of representative genomic data from the GTDB database and preprocessing flowchart